The five best imaging techniques for gentrification research are aerial time-lapse photography, thermal mapping, multispectral imaging, LiDAR scanning, and hyperspectral sensing. Each method offers unique insights into urban transformation. You'll capture large-scale changes with aerial time-lapse, track energy patterns through thermal mapping, analyze spectral data with multispectral imaging, create 3D models using LiDAR, and gather detailed surface information via hyperspectral sensing. These advanced technologies provide unprecedented views of neighborhood shifts, from building density to vegetation cover. They'll help you quantify and visualize gentrification processes with remarkable precision. Exploring these techniques further will reveal their full potential in urban studies.
Aerial Time-Lapse Photography
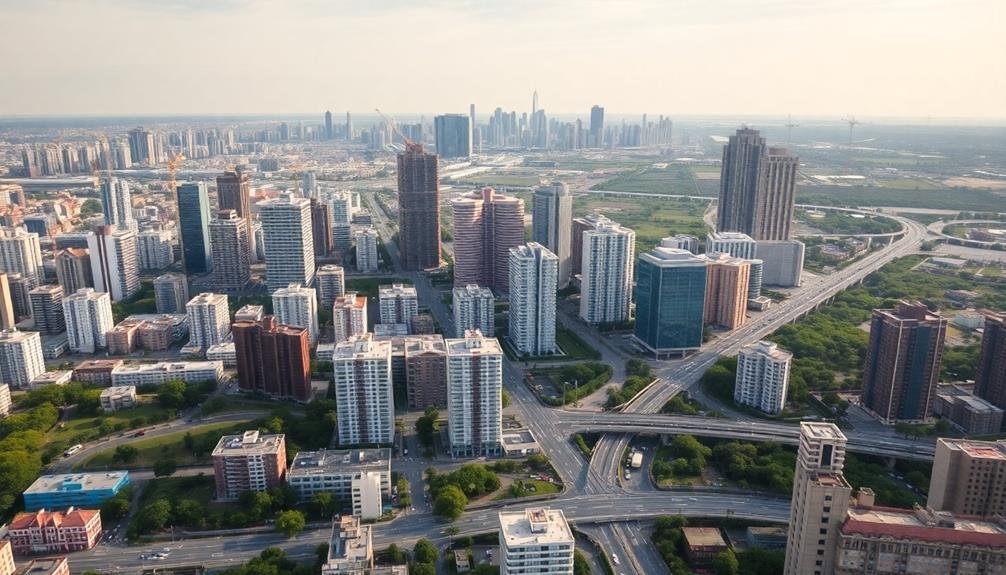

Soaring above urban landscapes, aerial time-lapse photography offers a unique perspective on gentrification processes. This technique allows you to capture large-scale changes in neighborhoods over extended periods. By using drones or aircraft, you'll collect high-resolution images at regular intervals, typically spanning several years.
To implement this method, you'll need to establish fixed flight paths and consistent camera settings. This guarantees your images are comparable across time. You'll then stitch these photos together to create a seamless visual narrative of urban transformation.
Aerial time-lapse photography reveals patterns that might be invisible from the ground. You'll observe changes in building density, green spaces, and infrastructure development. This birds-eye view helps you identify areas experiencing rapid gentrification and those resisting change.
When analyzing your time-lapse footage, pay attention to subtle indicators like roof renovations, new construction, and changes in parking patterns. These can signal shifts in neighborhood demographics and economic status.
While powerful, this technique has limitations. It doesn't capture street-level details or social interactions. You'll need to combine it with other research methods for a thorough understanding of gentrification processes.
Thermal Mapping
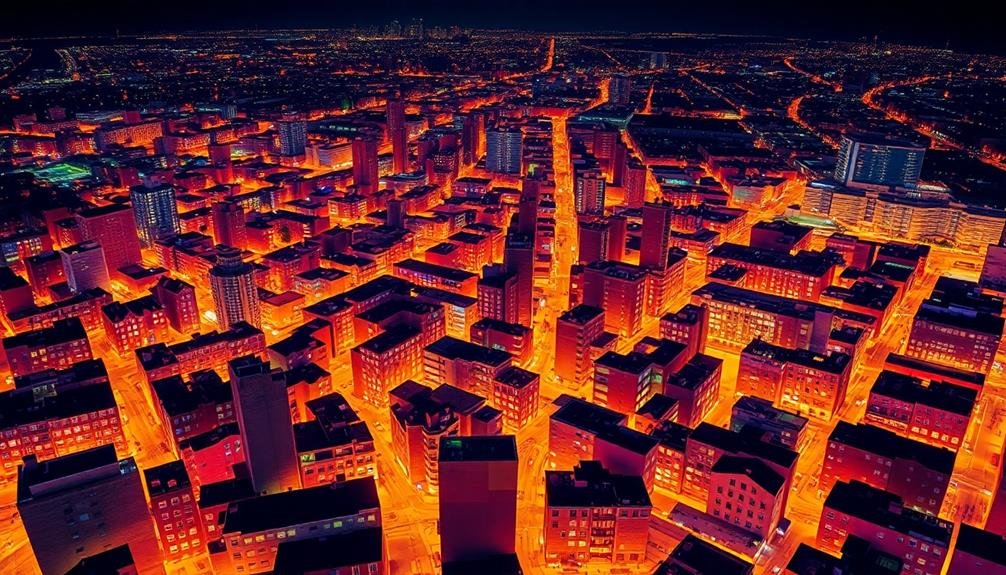

Frequently overlooked, thermal mapping offers a unique perspective on gentrification processes. You'll find this technique particularly useful for tracking energy consumption patterns across neighborhoods over time. By capturing infrared images, you can visualize heat signatures from buildings and infrastructure, revealing valuable insights into urban development and socioeconomic changes.
As gentrification unfolds, you'll notice shifts in thermal patterns. Newly renovated or constructed buildings often exhibit different heat profiles compared to older structures. You can observe increased energy efficiency in gentrified areas, indicated by lower heat loss. Conversely, you might detect higher heat signatures in rapidly developing zones due to increased air conditioning usage or the urban heat island effect.
You'll also spot changes in industrial areas, as warehouses transform into loft apartments or tech hubs. These conversions typically result in altered thermal footprints.
Multispectral Imaging
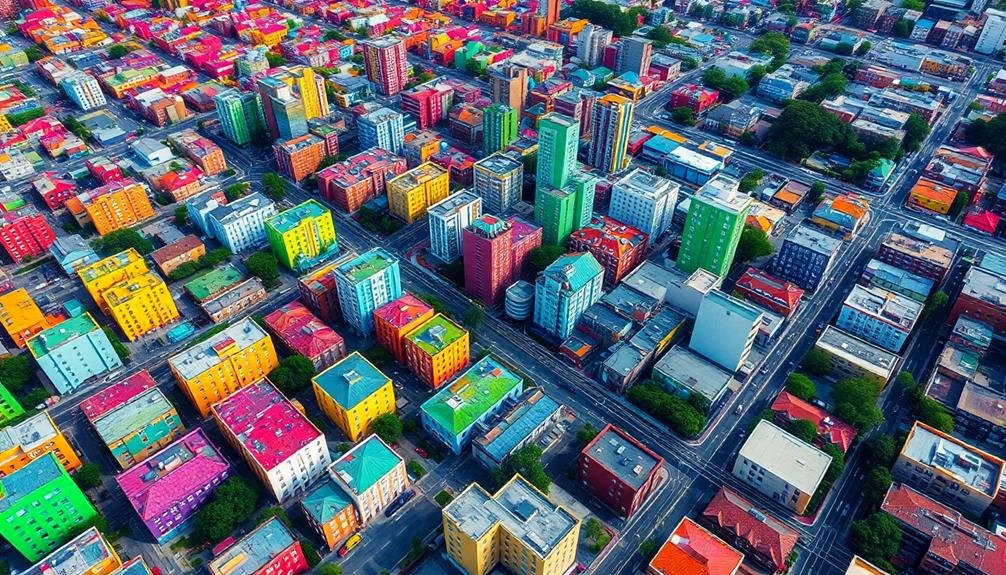

Versatility defines multispectral imaging in gentrification research. You'll find this technique captures data across multiple spectral bands, providing a wealth of information about urban landscapes. By analyzing these various wavelengths, you can identify changes in building materials, vegetation cover, and land use patterns that often accompany gentrification processes.
When you're using multispectral imaging, you'll be able to detect subtle shifts in neighborhood composition. You can track the replacement of older structures with newer ones, the increase in green spaces, or the expansion of commercial areas. The technique allows you to quantify these changes over time, giving you a thorough view of neighborhood transformation.
You'll also appreciate how multispectral imaging helps you identify socioeconomic indicators. By examining spectral signatures, you can infer information about property values, energy consumption, and even population density. This data enables you to create detailed maps of gentrification trends, highlighting areas undergoing rapid change.
Moreover, you'll find that multispectral imaging integrates well with other research methods. It complements traditional surveys and statistical analyses, providing a visual dimension to your gentrification studies and enhancing your overall understanding of urban dynamics.
LiDAR Scanning
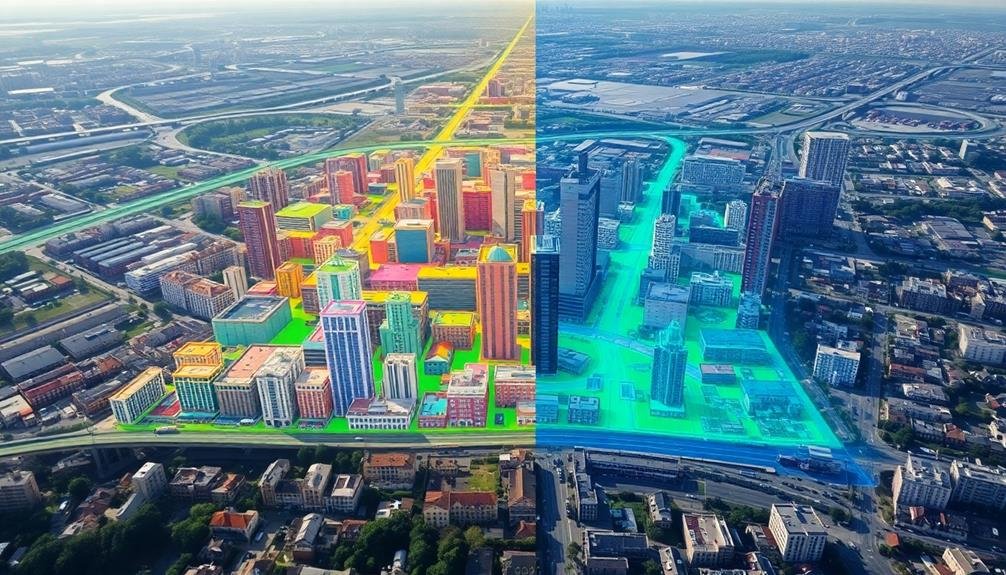
LiDAR scanning technology has revolutionized gentrification research by providing high-resolution 3D models of urban environments. You'll find that LiDAR, which stands for Light Detection and Ranging, uses laser pulses to measure distances and create detailed point clouds. These point clouds can be used to analyze changes in building heights, street layouts, and urban density over time.
When you're studying gentrification, LiDAR scanning offers several key advantages:
- Accuracy: LiDAR provides centimeter-level precision, allowing you to detect even subtle changes in the built environment.
- Temporal analysis: By comparing LiDAR scans from different time periods, you can quantify the pace and extent of urban development.
- Accessibility: LiDAR can capture data for large areas quickly, making it possible to study entire neighborhoods or cities efficiently.
You'll need specialized software to process and analyze LiDAR data, but the insights you'll gain are invaluable. By examining changes in building footprints, heights, and densities, you can identify areas undergoing rapid redevelopment – a key indicator of gentrification.
LiDAR data can also be combined with other imaging techniques, such as multispectral imaging, to provide a thorough view of urban change.
Hyperspectral Sensing
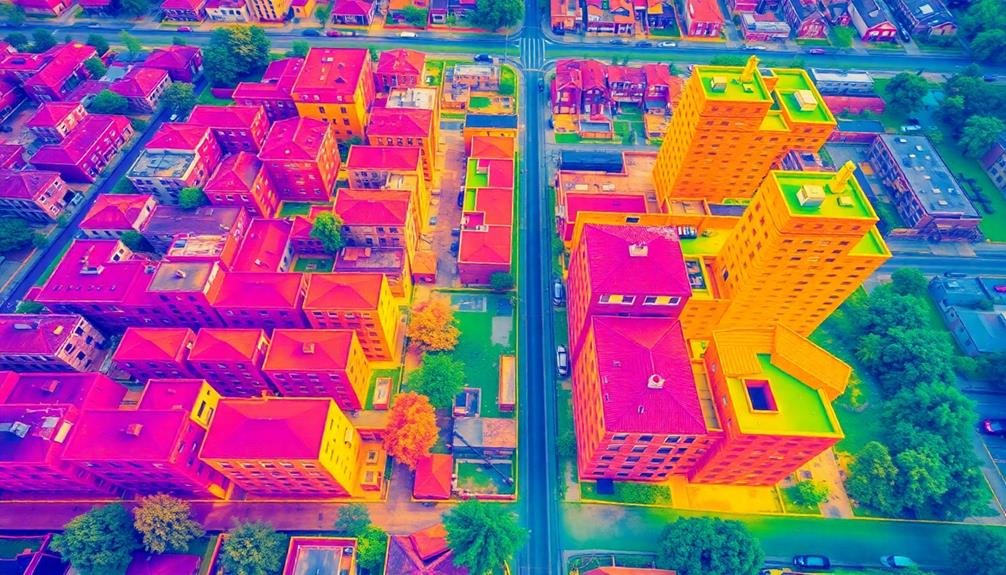

Numerous gentrification researchers are turning to hyperspectral sensing as a powerful tool for analyzing urban landscapes. This advanced imaging technique captures data across hundreds of narrow spectral bands, allowing you to detect subtle changes in urban environments that might indicate gentrification processes.
You'll find hyperspectral sensing particularly useful for identifying changes in building materials, vegetation health, and surface characteristics. It can help you spot new construction, renovations, and landscaping improvements that often accompany gentrification. By analyzing the spectral signatures of different surfaces, you can track the spread of high-end materials or the replacement of older structures with newer ones.
Moreover, you can use hyperspectral data to assess changes in air and water quality, which may correlate with neighborhood transformation. This technique also enables you to monitor vegetation patterns, potentially revealing shifts in urban green spaces or the introduction of non-native plant species in gentrifying areas.
To make the most of hyperspectral sensing, you'll need to combine it with other data sources and ground-truthing. It's a complex but rewarding method that can provide unique insights into the physical manifestations of gentrification processes.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Ethical Considerations Impact the Use of Imaging Techniques in Gentrification Research?
You'll need to reflect on privacy concerns when using imaging techniques. You should obtain informed consent, protect individual identities, and avoid stigmatizing communities. It's essential you're transparent about your methods and intentions throughout your research.
What Are the Cost Implications of Implementing These Advanced Imaging Technologies?
You'll find that implementing advanced imaging technologies can be quite costly. You're looking at expenses for equipment, software, training, and data storage. Don't forget ongoing maintenance costs. It's a significant investment, but can yield valuable insights.
How Can Researchers Integrate Social Media Data With Imaging Techniques for Gentrification Studies?
You can combine social media data with imaging techniques by geotagging posts, analyzing sentiment in neighborhood discussions, and overlaying this information on satellite or street view images to visualize gentrification trends and community reactions.
What Are the Limitations of Using Imaging Techniques in Densely Populated Urban Areas?
You'll face challenges using imaging in dense urban areas. Tall buildings obstruct views, shadows create data gaps, and rapid changes make images quickly outdated. It's also hard to capture social dynamics and interior transformations through visuals alone.
How Do Weather Conditions Affect the Accuracy of Different Imaging Techniques?
You'll find that weather greatly impacts imaging accuracy. Rain and fog can obscure optical sensors, while wind affects thermal imaging. Cloud cover limits satellite imagery. You'll need to take into account these factors when planning data collection.
In Summary
You've now explored five powerful imaging techniques for gentrification research. From aerial time-lapse photography to hyperspectral sensing, these tools offer unique insights into urban change. They'll help you visualize shifts in land use, building density, and neighborhood composition over time. Remember, combining multiple methods will give you the most thorough view. As you apply these techniques, you'll gain a deeper understanding of gentrification's complex spatial dynamics and impacts on communities.

As educators and advocates for responsible drone use, we’re committed to sharing our knowledge and expertise with aspiring aerial photographers.




Leave a Reply