To optimize search areas for SAR missions, start by analyzing terrain using satellite imagery and establishing probability zones. Consider the last known location and assess weather conditions that may affect the search. Utilize historical search data to inform your strategy and create grid search patterns for systematic coverage. Implement thermal imaging technology to enhance detection capabilities, especially in low-visibility conditions. Coordinate closely with ground teams to guarantee thorough coverage and adapt your search based on new findings. By combining these techniques, you'll maximize your chances of a successful rescue operation. These tips are just the beginning of a more effective SAR approach.
Analyze Terrain Using Satellite Imagery

Zeroing in on the search area begins with analyzing terrain using satellite imagery.
You'll want to access high-resolution satellite images of the region where the missing person was last seen. These images provide a bird's-eye view of the landscape, allowing you to identify key features that could impact the search.
Look for natural barriers like rivers, cliffs, or dense forests that might limit movement. Identify potential shelter areas, water sources, and clearings where a lost individual might seek help.
Pay attention to elevation changes, as they can affect travel speed and direction. Note any man-made structures, roads, or trails that could serve as reference points or potential destinations.
Use mapping software to overlay grid patterns on the satellite imagery. This will help you segment the search area into manageable sections.
Consider seasonal changes that might affect vegetation cover or water levels. If possible, compare recent images with older ones to spot any significant landscape changes.
Establish Probability Zones
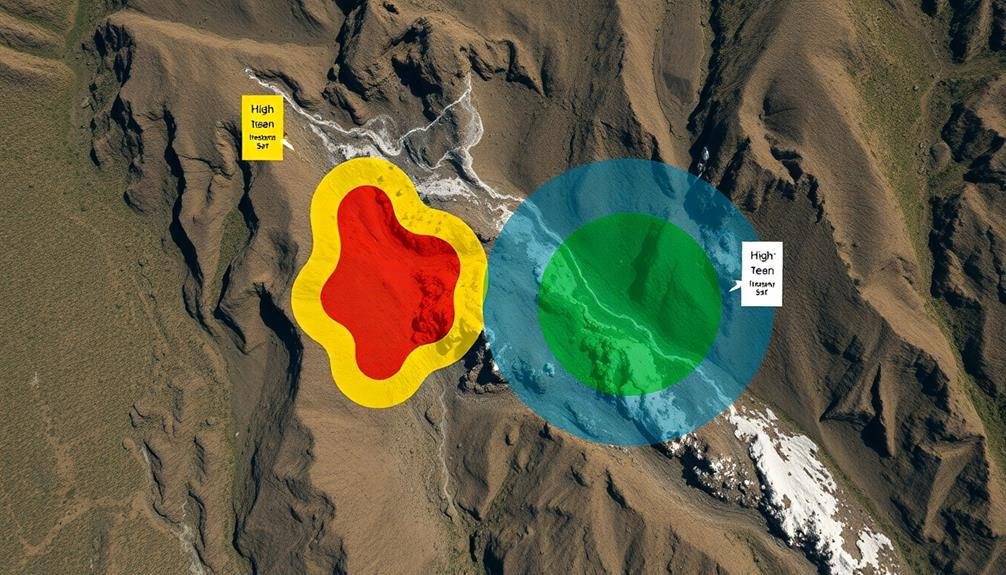
Establish probability zones by defining high-likelihood search regions based on your initial data and analysis.
You'll want to use terrain analysis tools to identify areas that match the victim's last known location and potential routes.
Consider the victim's likely behavior patterns, such as seeking shelter or following natural pathways, to further refine your probability zones.
Define High-Probability Search Regions
Once you've gathered all available information about the missing person or vessel, it's crucial to define high-probability search regions. These areas are where you'll focus your initial search efforts, maximizing the chances of a successful rescue.
To identify these regions, analyze the data you've collected, including last known location, weather conditions, and terrain features.
Consider the subject's capabilities, such as their physical fitness or vessel characteristics, to determine how far they might've traveled. Factor in any potential hazards or obstacles that could influence their movement. Use this information to create a map overlay highlighting the most likely areas where the subject may be found.
To further refine your high-probability search regions:
- Prioritize areas with natural shelter, water sources, or other survival necessities
- Identify potential routes the subject might've taken based on their known intentions or habits
- Consider areas where previous successful rescues have occurred in similar situations
Use Terrain Analysis Tools
With terrain analysis tools at your disposal, you can establish more precise probability zones within your high-priority search regions. These tools help you factor in landscape features, vegetation density, and elevation changes that might influence a lost person's movement or survival chances.
Start by using digital elevation models (DEMs) to create slope and aspect maps. These will highlight areas that are more challenging to traverse or might funnel movement in specific directions. Next, analyze vegetation cover using satellite imagery or LiDAR data to identify dense forests, open fields, or water bodies.
| Tool | Purpose | Data Source |
|---|---|---|
| DEM | Elevation analysis | USGS, NASA |
| Slope Map | Identify steep areas | Derived from DEM |
| Aspect Map | Determine sun exposure | Derived from DEM |
| Vegetation Map | Assess cover density | Satellite imagery |
Combine these layers with known behavioral patterns of lost persons in similar terrains. You'll create a composite map that highlights areas where the missing individual is most likely to be found. Remember to take into account seasonal changes, weather conditions, and the person's physical capabilities when interpreting these probability zones.
Consider Victim Behavior Patterns
Victim behavior patterns play a crucial role in establishing probability zones for SAR missions. You'll need to analyze historical data and research on lost person behavior to predict likely movements and locations.
Consider factors such as age, physical condition, mental state, and outdoor experience when evaluating potential victim actions.
To effectively use victim behavior patterns:
- Study statistical models: Familiarize yourself with established models like the International Search and Rescue Incident Database (ISRID) to understand common behaviors in different terrains and situations.
- Create subject profiles: Develop detailed profiles of the missing person, including their skills, habits, and last known intentions. This information will help you tailor your search strategy to their specific characteristics.
- Map likely routes: Based on the subject's profile and terrain analysis, identify probable paths and destinations. Pay special attention to natural lines of drift, such as ridgelines or water courses.
Consider Last Known Location

When planning a search and rescue (SAR) mission, the last known location (LKL) of the missing person is a critical starting point. You'll want to gather as much information as possible about the LKL, including exact coordinates, time last seen, and any relevant details about the surrounding area.
Use the LKL to create a probability map, which helps you prioritize search areas. Start with a tight radius around the LKL and gradually expand outward. Consider factors like terrain, weather conditions, and the missing person's physical capabilities when determining search zones.
Here's a quick reference guide for LKL-based search planning:
| Distance from LKL | Search Priority | Recommended Resources |
|---|---|---|
| 0-1 mile | Highest | Ground teams, K9 units |
| 1-3 miles | High | ATVs, drones |
| 3-5 miles | Medium | Helicopters, grid search |
| 5+ miles | Low | Aircraft, wide-area scan |
Remember to reassess your search areas regularly as new information becomes available. The LKL serves as your anchor point, but don't let it limit your search if evidence suggests the missing person has moved beyond the initial search zones.
Assess Weather Conditions

Weather conditions play an essential role in shaping your search strategy and can considerably impact the safety and effectiveness of your SAR mission.
You'll need to carefully assess current and forecasted conditions before deploying your team. Consider wind speed and direction, as they can affect scent trails for search dogs and influence the drift of any floating objects.
Precipitation can obscure visual clues and make terrain more treacherous, while temperature extremes may limit search duration or require specialized equipment.
To optimize your search area based on weather conditions:
- Consult multiple weather sources, including local meteorologists and on-site observations, to get a thorough understanding of the current and expected conditions.
- Use weather data to adjust your search patterns, prioritizing areas that are less affected by adverse conditions or where the weather might've pushed the missing person or evidence.
- Factor in how weather might influence the subject's behavior, such as seeking shelter from storms or moving towards water sources in hot conditions.
Utilize Historical Search Data

You'll gain valuable insights by analyzing past successful searches in your area.
Identify common terrain patterns where victims were frequently found to narrow your focus.
Map out locations of frequent incidents to establish potential hotspots and optimize your search strategy.
Analyze Past Successful Searches
Countless successful search and rescue (SAR) missions can provide valuable insights for optimizing future operations. By analyzing past successful searches, you'll uncover patterns and strategies that have proven effective in locating missing persons or assets.
Focus on extracting key information from these missions, such as the initial search area, resources deployed, and time to successful recovery.
When reviewing past searches, pay close attention to:
- Environmental factors: Terrain types, weather conditions, and seasonal variations that influenced search outcomes
- Subject behavior: Common patterns in lost person behavior, including age groups, mental states, and survival skills
- Search techniques: Effective methods used, such as grid searches, tracking, or air support
Use this data to refine your search area predictions and resource allocation. Identify trends in successful search locations relative to the last known position or point last seen.
Consider creating a database of successful searches, categorizing them by terrain, subject profile, and search methods. This repository will serve as a valuable reference for future missions, allowing you to quickly access relevant historical data and apply proven strategies to new SAR operations.
Identify Common Terrain Patterns
Building on historical search data, identifying common terrain patterns is essential for optimizing SAR missions.
You'll want to analyze past searches to recognize recurring geographical features where lost individuals are frequently found. Look for patterns in elevation, vegetation density, water sources, and natural barriers.
Pay attention to common terrain traps, such as steep ravines, dense thickets, or confusing trail intersections. These areas often disorient hikers and should be prioritized in your search efforts.
Note how different terrains affect travel speed and direction, as this can help predict a subject's potential location.
Don't forget to evaluate seasonal changes in terrain patterns. A dry riverbed in summer might become a dangerous water obstacle in spring.
Also, examine how weather conditions interact with specific terrains, potentially creating hazardous situations that influence a subject's behavior.
Map Frequent Incident Locations
Mapping frequent incident locations forms the backbone of efficient SAR operations. By analyzing historical data, you'll identify areas where incidents occur more often, allowing you to prioritize search efforts effectively.
Start by gathering incident reports from previous missions and plot them on a map. Look for patterns and clusters that emerge over time.
Once you've identified these hotspots, consider the following factors:
- Seasonal variations: Some areas may be more prone to incidents during specific times of the year due to weather conditions or popular activities.
- Terrain complexity: Challenging terrains often lead to higher incident rates, so pay close attention to these areas.
- Access points: Many incidents occur near trailheads, campsites, or other popular entry points to wilderness areas.
Use this information to create a heat map of incident frequencies. This visual representation will help you quickly assess which areas require more attention during SAR missions.
Update your maps regularly as new data becomes available, and share this information with your team. By focusing on these high-probability areas, you'll increase your chances of locating missing persons more quickly and efficiently.
Deploy Multiple Drone Types

Diversity in aerial assets can greatly enhance search and rescue (SAR) operations.
When you're planning your mission, consider deploying multiple types of drones to cover various search scenarios. Fixed-wing drones offer extended flight times and can quickly survey large areas, making them ideal for initial sweeps. They're particularly useful in open terrain or when searching for missing hikers or vehicles.
Rotary-wing drones, on the other hand, excel at hovering and maneuvering in tight spaces. They're perfect for searching dense forests, rocky canyons, or urban environments. These drones can get closer to the ground and provide detailed imagery of specific locations.
Don't forget about specialized drones equipped with thermal cameras or infrared sensors. They can detect heat signatures, making them invaluable for nighttime searches or locating individuals in challenging visibility conditions.
Create Grid Search Patterns
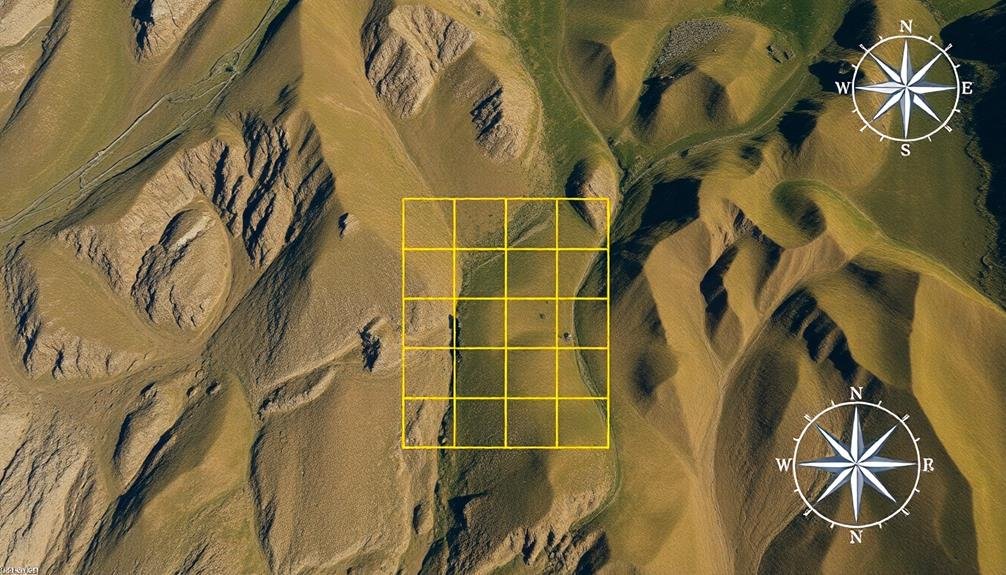
Grid search patterns form the backbone of efficient SAR operations. When creating these patterns, you'll need to take into account the terrain, weather conditions, and the missing person's last known location.
Start by dividing the search area into manageable sectors, then assign teams to systematically cover each section.
To optimize your grid search pattern:
- Use parallel track patterns for flat, open areas. This involves searchers moving in straight lines, parallel to each other, covering the entire area methodically.
- Implement contour search patterns for hilly or mountainous terrain. Teams follow the natural contours of the land at different elevations, guaranteeing thorough coverage of slopes and valleys.
- Adopt expanding square patterns when you have a specific point of interest. Begin at the center and expand outward in a square formation, gradually increasing the search area.
Remember to adjust your grid size based on visibility and terrain complexity. In dense forests or rugged landscapes, you'll need tighter grid patterns to make certain nothing is missed.
Always maintain clear communication between search teams and coordinate their movements to avoid overlap or gaps in coverage. By creating effective grid search patterns, you'll greatly enhance your chances of a successful SAR mission.
Implement Thermal Imaging Technology

You'll find thermal imaging technology to be a game-changer in SAR missions.
It allows you to detect hidden heat signatures, even in challenging conditions, greatly enhancing your nighttime search capabilities.
Detect Hidden Heat Signatures
To enhance search efficiency, thermal imaging technology proves invaluable in detecting hidden heat signatures. You'll find that this advanced equipment can reveal the presence of individuals who might be concealed from visual detection. By identifying heat sources in various environments, you're able to locate survivors even in challenging conditions like dense forests or debris-filled areas.
When using thermal imaging devices, consider these key factors:
- Temperature differentials: Look for anomalies in heat patterns that stand out from the surrounding environment. A human body typically emits more heat than its surroundings, making it easier to spot.
- Time of day: Early morning or late evening are often the best times for thermal imaging, as the temperature contrast between bodies and the environment is more pronounced.
- Environmental conditions: Be aware that rain, fog, or dense vegetation can affect thermal imaging effectiveness. Adjust your search patterns accordingly.
You'll need to interpret the thermal data correctly, distinguishing between human heat signatures and other warm objects like animals or machinery.
Enhance Nighttime Search Capabilities
Building on the advantages of thermal imaging, this technology becomes even more valuable during nighttime operations. You'll find that thermal imaging cameras can detect heat signatures in complete darkness, giving you a considerable advantage in low-light conditions.
To enhance your nighttime search capabilities, invest in high-quality thermal imaging devices designed for SAR missions.
When implementing thermal imaging for nighttime searches, train your team to interpret thermal images accurately. You'll need to distinguish between human heat signatures and other warm objects in the environment.
Use a combination of handheld thermal cameras and drone-mounted thermal sensors to cover larger areas efficiently.
Don't forget to integrate thermal imaging with other nighttime search tools, such as night vision goggles and powerful searchlights. This multi-layered approach will help you detect missing persons who may be hidden or unconscious.
Remember to adjust your search patterns to account for the limited field of view of thermal cameras. Sweep areas systematically, paying extra attention to potential shelter spots where a person might seek refuge.
Pinpoint Survivors' Locations
Implementing thermal imaging technology revolutionizes the process of pinpointing survivors' locations during SAR missions.
You'll find that thermal cameras detect heat signatures emitted by human bodies, making them invaluable tools for locating survivors in various environments and conditions. These devices work effectively in darkness, through smoke, and even in dense vegetation, greatly enhancing your search capabilities.
To maximize the effectiveness of thermal imaging in your SAR operations:
- Equip your search teams with handheld thermal cameras for ground-based searches, allowing them to scan large areas quickly and efficiently.
- Integrate thermal imaging systems into your aerial assets, such as helicopters or drones, to cover vast areas and identify potential survivor locations from above.
- Train your personnel thoroughly in interpreting thermal images, as different heat signatures can indicate various scenarios, such as recent movement or the presence of animals.
Coordinate With Ground Teams
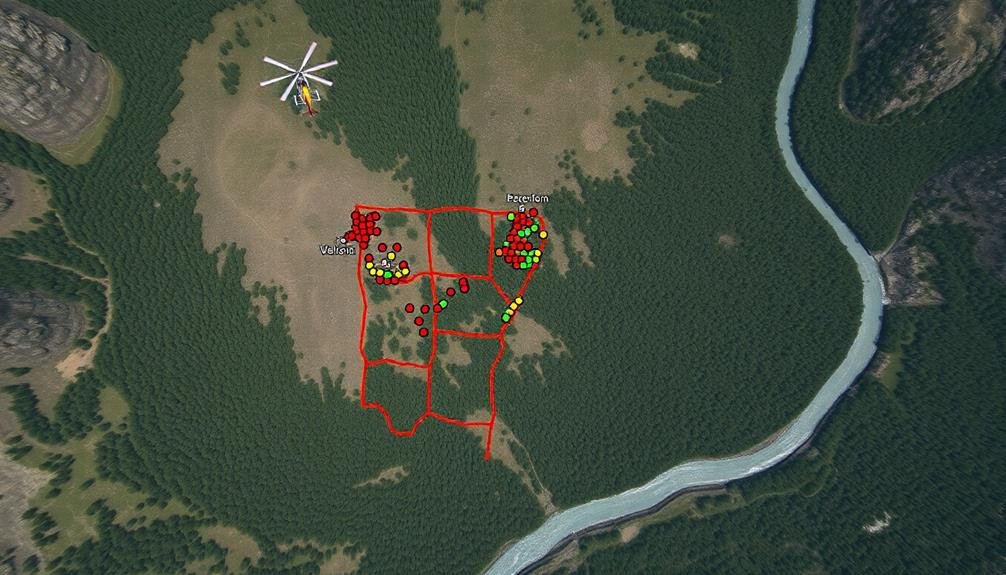
Effective coordination between air and ground teams is essential for successful search and rescue (SAR) operations. You'll need to establish clear communication channels and protocols to guarantee seamless information exchange. Use a shared radio frequency or satellite communication system to maintain constant contact between air and ground units.
Brief your ground teams on the search area's boundaries and specific sectors they'll be covering. Provide them with detailed maps, GPS coordinates, and any relevant terrain information. You should also share aerial observations and potential survivor locations with ground teams to guide their efforts more effectively.
Coordinate your search patterns to avoid overlap and maximize coverage. Assign ground teams to areas that are difficult to assess from the air, such as dense forests or steep ravines. Use air support to guide ground teams through challenging terrain and to quickly verify potential sightings.
Establish regular check-in times for status updates and to adjust search strategies as needed. Share real-time weather conditions and any changes in the search area with ground teams.
Adapt Search Based on Findings
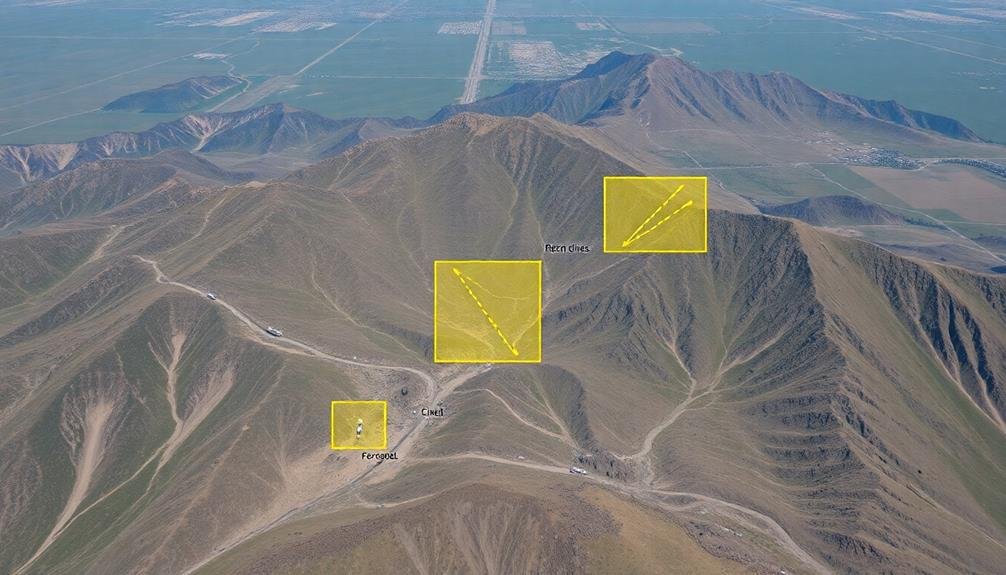
Search flexibility is essential for SAR missions. As you gather information during the operation, you'll need to adjust your search strategy accordingly. Don't stick rigidly to your initial plan if new evidence suggests a different approach. Instead, be prepared to shift your focus based on clues, witness reports, or environmental changes.
When adapting your search, consider these key factors:
- Terrain changes: If you discover unexpected obstacles or hazards, modify your search pattern to guarantee thorough coverage while maintaining team safety.
- Weather conditions: Adjust your tactics if weather impacts visibility, mobility, or the subject's likely behavior.
- Time constraints: As the mission progresses, reassess your priorities and concentrate efforts on high-probability areas.
Use real-time data from search teams to refine your approach. If searchers find footprints, personal items, or other signs of the subject's presence, concentrate resources in that vicinity. Conversely, if certain areas yield no results, consider reallocating teams to more promising locations.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do You Prioritize Search Areas When Multiple Locations Are Reported?
You'll prioritize search areas by evaluating the reliability of each report, considering terrain and weather conditions, evaluating potential survivor movements, and factoring in time since last known location. Start with the most promising areas first.
What Role Does Social Media Play in Modern Search and Rescue Missions?
Social media plays an essential role in modern search and rescue. You'll find it's used to gather information, spread alerts, coordinate volunteers, and track real-time updates. It's become an invaluable tool for expanding search efforts quickly.
How Can Machine Learning Algorithms Improve Search Area Optimization?
You can leverage machine learning algorithms to analyze historical data, terrain features, and weather patterns. They'll predict likely locations, prioritize search areas, and adapt in real-time as new information becomes available, considerably improving your search efficiency.
What Are the Legal Considerations When Conducting Searches on Private Property?
You'll need to obtain permission or a warrant to search private property. It's essential to respect property rights while conducting searches. If time is critical, you can seek emergency exceptions or exigent circumstances to proceed.
How Do You Determine When to Scale Back or Terminate a Search Operation?
You'll need to assess multiple factors to decide when to scale back or end a search. Consider search duration, resources available, weather conditions, probability of survival, and new information. Consult with team leaders and officials before making decisions.
In Summary
You've got the tools to optimize your search areas for SAR missions. Remember, it's about smart planning and adaptability. Use technology, historical data, and expert knowledge to your advantage. Stay flexible and adjust your strategy as new information comes in. By following these tips, you'll improve your chances of a successful search and rescue operation. Keep honing your skills and stay prepared for the next mission.

As educators and advocates for responsible drone use, we’re committed to sharing our knowledge and expertise with aspiring aerial photographers.




Leave a Reply